
Mobility as a Service Market By Service Type (Ride Hailing, Car Sharing, Others), By Operating System (Android, iOS, Others), By Transportation Type (Private, Public), By Region And Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, And Forecast 2023-2032
-
13776
-
June 2023
-
103
-
-
This report was compiled by Correspondence Linkedin | Detailed Market research Methodology Our methodology involves a mix of primary research, including interviews with leading mental health experts, and secondary research from reputable medical journals and databases. View Detailed Methodology Page
-
Report Overview
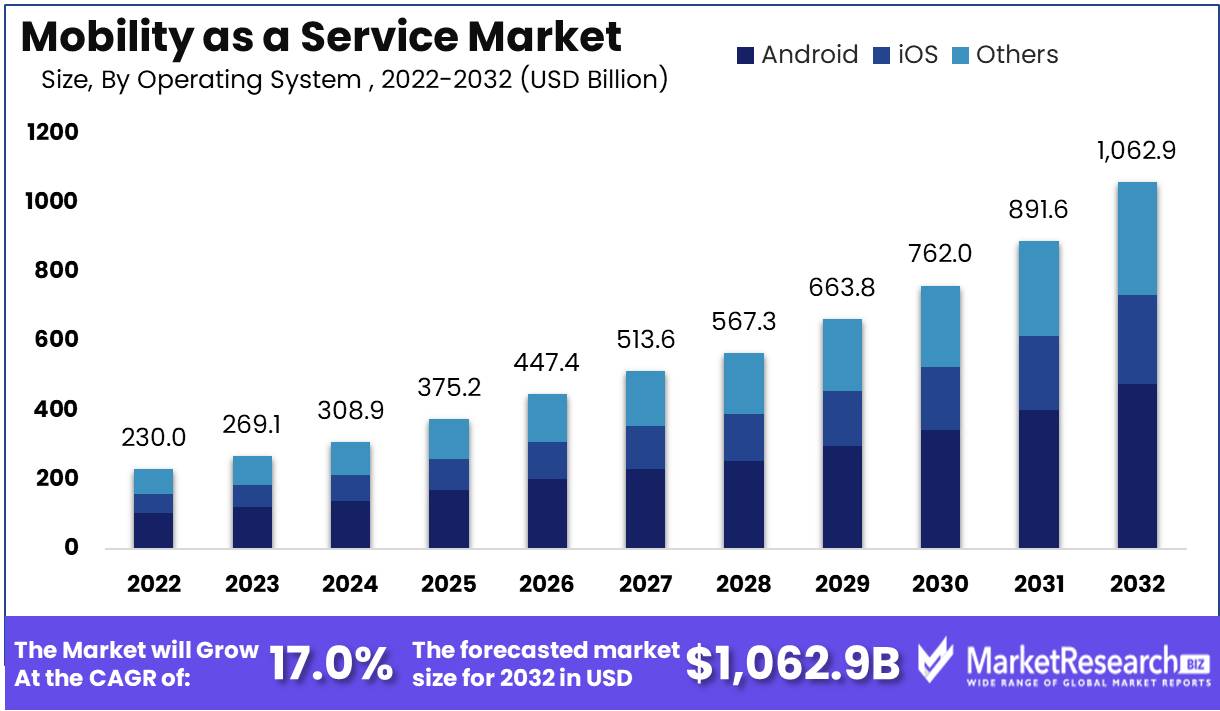
Mobility as a Service Market size is expected to be worth around USD 1,062.9 Bn by 2032 from USD 230.0 Bn in 2022, growing at a CAGR of 17.0% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2032.
The Mobility as a Service (MaaS) market has changed and grown a lot in recent years. MaaS is the process of putting together different transportation services on a single platform so that people can get around easily and quickly. It aims to offer an alternative to owning a private car by giving people a lot of different ways to get around, like public transportation, ride-hailing, bike-sharing, car-sharing, and more.
The MaaS idea has become popular because it could change the way people get around cities and help solve problems like traffic jams, pollution, and a lack of parking spots. MaaS platforms let users plan and book their trips using just one app or service. They do this by combining different types of transportation and giving real-time information on available routes, prices, and dates. This all-around method to mobility gives people more freedom and flexibility to choose the most efficient and cost-effective way to get where they need to go.
One of the best things about MaaS is that it can make urban transportation systems more efficient as a whole. MaaS can help cut down on the number of private cars on the road by encouraging the use of shared means of transportation and optimizing routes. This will reduce traffic and improve the air quality. MaaS could also help underserved areas get better access to transportation services by filling in gaps in public transit networks and giving cheap alternatives to owning a car.
Driving factors
Urbanization
One of the main forces behind the MaaS market is urbanization. Traditional modes of transportation, such as private cars, buses, and trains, are becoming less and less sustainable as our towns continue to grow and become more crowded. Traffic jams, smog, and a lack of parking are all contributing factors to a rise in demand for more efficient and environmentally friendly modes of transportation.
In reaction to these problems, a number of MaaS solutions have come up that allow commuters to use multiple modes of transportation in a way that works well together. Most of the time, these solutions involve using mobile apps, real-time data, and predictive analytics to find the best travel routes and cut down on journey time.
Digital Advancements
The MaaS market is also being driven by digital changes. The widespread use of smartphones, mobile apps, and onboard technologies has created new possibilities for service providers to offer cutting-edge transportation solutions that are highly personalized and tailored to each individual's needs.
This is shown by the fact that ride-sharing services like Uber and Lyft have changed the way people think about transportation. By using real-time data and algorithms to match riders with nearby drivers, these services have created a new kind of on-demand transportation that is convenient, affordable, and easy to use.
Demand for Shared Mobility
The growing demand for shared mobility is another thing that is making the MaaS market grow. This trend is caused by a number of things, such as changes in how people feel about owning cars, growing worry about how transportation affects the environment, and the need to make more efficient use of limited transportation infrastructure.
As people look for more affordable and environmentally friendly forms of transportation, shared mobility services like car-sharing, bike-sharing, and ride-sharing have become more common. Most of the time, these services use shared vehicles that can be used on a pay-per-use basis. This makes it easy for commuters to get around without having to deal with the costs and headaches of owning a car.
Restraining Factors
Regulatory Challenges
The MaaS market faces numerous regulatory challenges in various regions, which eventually slows its growth. The rules governing the use of personal data, safety standards, and legal framework for ride-sharing services are frequently intricate and vary from country to country. For example, the new General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) of the European Union says that businesses must get specific permission from users before using their data. If businesses don't follow GDPR, they can face serious fines. At the local, regional, and international levels, MaaS businesses must ensure compliance while facing regulatory challenges.
Data Privacy Concerns
Privacy advocates pay close attention to how the MaaS market handles data collection and sharing. Concerns about user privacy have been raised by the collection of user data, like where they are and how they move. The sharing of customer data with third-party service providers and other MaaS companies has also resulted in a number of data breaches and the exposure of private user information. For the MaaS market to reach its full growth potential, it needs to answer concerns about data security, data use, and data sharing.
Infrastructure Limitations
The MaaS market needs a solid infrastructure that makes it easy for people, things, and services to move around. But many places don't have the right infrastructure to support the MaaS ecosystem. Some infrastructure problems that slow the growth of MaaS include not enough or old transportation infrastructure, not enough charging infrastructure for electric vehicles, and not enough public transportation choices. The ability of MaaS providers to provide a smooth user experience is constrained by inadequate infrastructure, which also raises the cost of operations.
Service Type Analysis
The huge growth of ride-hailing can be attributed to a number of factors, including ease of use, low cost, and cutting-edge technology. With the arrival of GPS-enabled smartphones, ride-hailing services have become more accessible, affordable, and reliable than standard taxi services. Commuters can book a ride in real time, find out where the driver is, and pay for it using ride-hailing apps on their mobile devices.
Also, the competition between ride-hailing companies has led to better services, lower prices, and better deals for customers. Because of this, the ride-hailing segment has become the choice of many commuters around the world.
One of the main factors in the growth of ride-hailing services is the fact that economies in emerging countries are getting stronger. The need for affordable and accessible transportation has grown as a result of more people moving to cities. In emerging economies, the middle class wants good services and is ready to pay for them. They can get an affordable, secure, and comfortable means of transportation that is specifically suited to their needs by using ride-hailing.
Operating System Analysis
Mobility As A Service Market Dominates Android Segment. In the MaaS market, Android has emerged as the most popular operating system, beating iOS and other proprietary systems. The success of the Android operating system can be attributed to a number of factors, including its affordability, open-source nature, and customization choices. Android is an open-source operating system. This means that anyone can use it and change it in any way they want. This has led to a big group of developers making apps and services that work on this platform.
Additionally, smartphones with Android operating systems are more affordable than iPhones, making them more accessible to a wider audience. Android is an operating system that is easier to use because users can change their devices to suit their needs.
The growing economic growth in emerging economies can also be attributed to the popularity of the Android operating system. The majority of customers in developing countries are very concerned about affordability, and smartphones powered by Android give them cheaper access to technology. The number of people in the middle class is growing in these countries, and they want and are willing to pay for good services. They can access other value-added services like payment gateways, location-based services, and real-time information thanks to Android-powered smartphones, which also give them a dependable mode of transportation.
Transportation Type Analysis
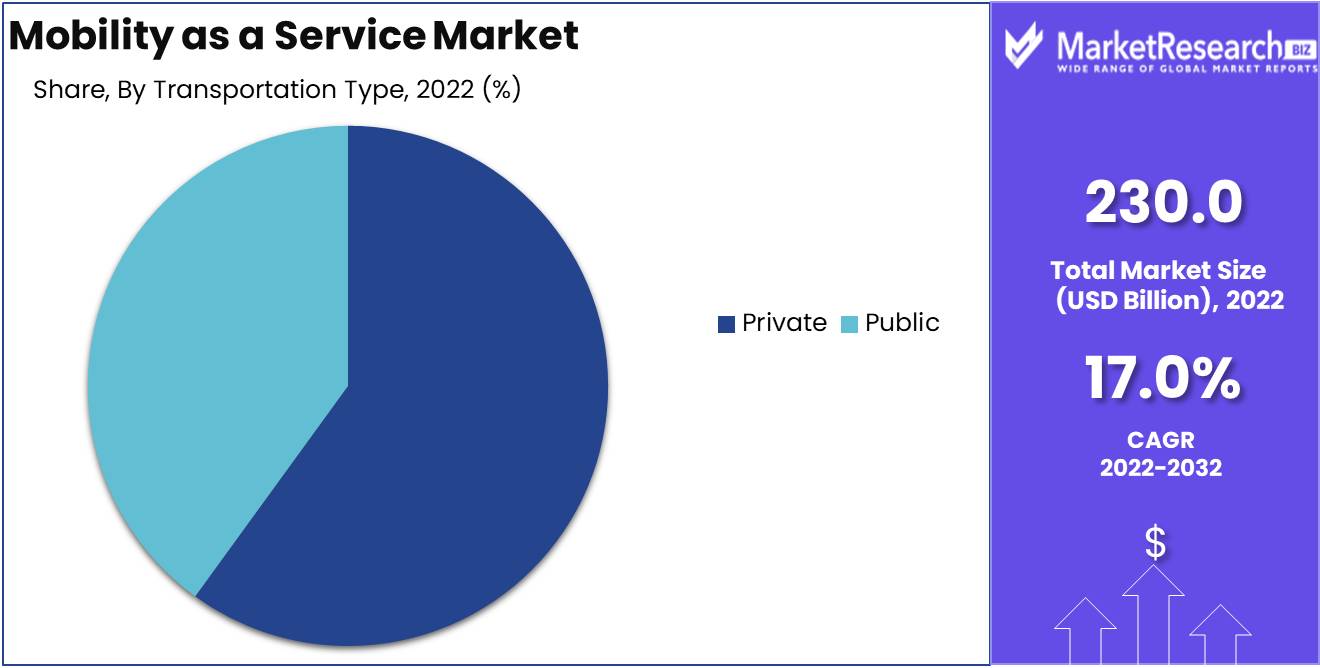
In the MaaS market, the private segment has emerged as the most popular form of transportation, surpassing public transportation and other modes. Cars, motorcycles, and other privately owned vehicles are part of the private segment.
Convenience, flexibility, and status symbol are just a few of the factors that can be attributed to the private segment's dominance. The flexibility to travel at their own pace, on their own terms, and without having to stick to a set plan is provided to commuters by private transportation. It also gives them a sense of independence and privacy, which they don't have when they take public transportation.
Also, in many cultures, having a car or motorcycle is a sign of wealth, and people are happy to pay more for it. This has led to the growth of private transportation services like ride-hailing, renting cars, and car-sharing.
Key Market Segments
By Service Type
- Ride Hailing
- Car Sharing
- Micromobility
- Bus Sharing
- Train Services
By Operating System
- Android
- iOS
- Others
By Transportation Type
- Private
- Public
By Solution Type
- Technology Platforms
- Payment Engines
- Navigation Solutions
- Telecom Connectivity Providers
- Ticketing Solutions
- Insurance Services
Growth Opportunity
Integration with Emerging Technologies
One of the main benefits of MaaS is its capacity to work with cutting-edge technologies like 5G, IoT, and AI to offer new and creative transportation options. For example, by utilizing 5G technology, MaaS providers can offer real-time, hyper-personalized transportation choices that take into account factors such as the user's location, traffic conditions, and the availability of various modes of transportation. MaaS could become a fully automated, on-demand transportation option that improves safety, efficiency, and convenience with the rise of self-driving vehicles.
Electric Vehicle Expansion
The rapid growth of electric vehicles (EVs) around the world is another important reason driving the growth of the MaaS market. In terms of lowering carbon emissions, improving air quality, and improving energy efficiency, EVs offer significant benefits over conventional gasoline-powered vehicles. MaaS providers can use EVs to offer green transportation choices that are sustainable and good for the environment. This meets the growing demand for green solutions. MaaS providers can offer a wider range of transportation choices, like e-bikes and e-scooters, which are great for short trips, by adding EVs to their services.
Ecosystem Collaboration for Comprehensive
MaaS is a complex, multi-faceted answer that needs collaboration between different stakeholders to build complete ecosystems that offer users end-to-end solutions. The government, transportation companies, internet companies, and service providers are all working together on this project. The key to making successful MaaS ecosystems is to make them interoperable, secure, and scalable, and to offer users a wide range of services that meet their changing needs. By working together well, stakeholders in the MaaS field can unlock exciting growth potential and create new and innovative transportation solutions.
Personalized Solutions
MaaS providers are focusing on giving personalized, customized solutions that meet the wants and preferences of each user. Personalized solutions can help MaaS providers stand out in a crowded market and offer users a better value proposition. By using data analytics, machine learning, and AI, MaaS providers can offer hyper-personalized transportation solutions that take into account factors like the user's location, journey history, preferred modes of transportation, and budget.
Latest Trends
Growth of Ride-Hailing and Car-Sharing Services
The urban transportation landscape has been transformed by ride-hailing services, which themselves are being transformed by newer technologies. Uber, Lyft, and Didi Chuxing, which are the top players in the industry, have built their brands and businesses around the desire for mobility-on-demand services. They do this by using smart devices to connect riders with drivers within minutes. Their business models are based on giving drivers new ways to make money and providing cheap, accessible, and practical alternatives to conventional transportation methods.
On the other hand, car-sharing services are becoming more and more popular in places all over the world. These services give you open, on-demand access to cars without having to own one or pay for it. In the car-sharing market, Zipcar, Turo, and Car2Go are the leaders. Customers have the ability to rent cars by minute, hour, or day from them.
Integration of Multiple Modes of Transportation in Mobility Platforms
The future of MaaS is one in which different modes of transportation are integrated into a single platform in a seamless manner. It makes it easier and easier for users to access, pay for, and use a variety of transportation modes, including public transit, ride-hailing, car-sharing, bike-sharing, and even e-scooters. Users can find the best way to get to their goals while saving time and money by combining different modes of transportation.
Transit and travel apps like Moovit, Citymapper, and Transit. app offers users multi-modal transport solutions that help them get around the city streets. In addition to integrating various modes of transportation into a single app, they offer real-time information on transit schedules, bike-sharing locations, and vehicle availability during rush hours. These solutions lessen traffic on the roads, save time, and make urban transportation more accessible for all.
Adoption of Mobile Payment Solutions in the MaaS Ecosystem
The MaaS ecosystem is built around giving users a seamless and unified experience, so the ability to pay for all transportation services through a single site is very important. With mobile payments, commuters don't have to take cash or multiple tickets to use different modes of transportation. Mobile payments are also very handy because you can make them through an app on your phone.
The mobile payment solutions let users combine different payment methods, like bank cards, digital wallets, and prepaid accounts, and download transactions straight to their phones. These payment methods have changed the world's payment system by making it easier, faster, and safer for users.
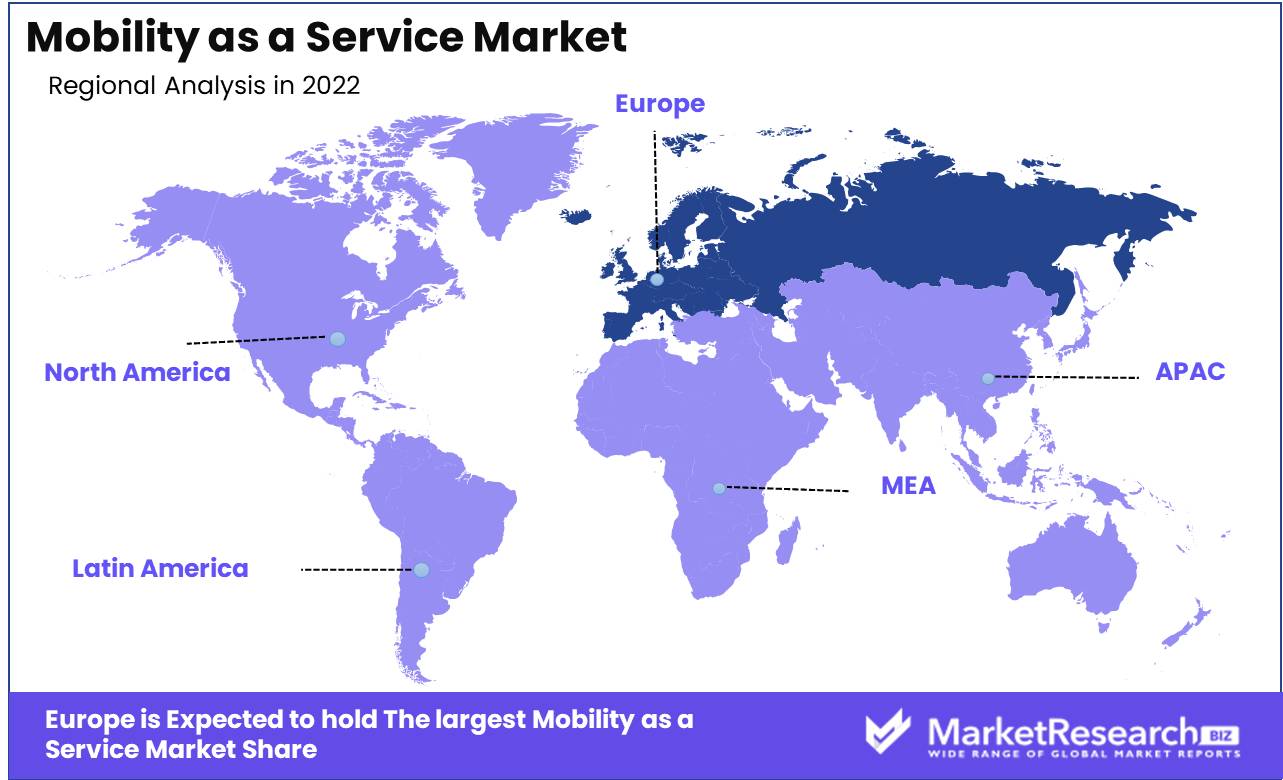
Regional Analysis
The Mobility as a Service Market is led by the Europe region. One of the main reasons why MaaS is so successful in Europe is that governments back it up so well. European countries have well-established transportation policies that are meant to reduce traffic and smog and make transportation easier to use. Many cities have also set up low-emission zones and improved their public transportation systems, making it easier for people to use MaaS services. Also, governments often give grants and funding to MaaS startups. This makes it easier for them to get started and grows innovation and growth.
MaaS has also been successful because different players in Europe's transportation business have worked together and made partnerships. Private companies, public groups, and even academic institutions have worked together to make MaaS systems that work well and meet the needs of different communities and demographics.
For example, a number of European startups have worked with public transportation companies to add their solutions to current mobility services. The result is that MaaS fits seamlessly into people's daily lives, making it easier than ever to use.
Europe is well-known for its technological progress, and the MaaS business is no different. The area has a strong track record of coming up with and adopting cutting-edge mobility solutions that are user-friendly, safe, and efficient. In Europe, MaaS solutions are powered by technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Advanced algorithms, simulation models, and data analytics platforms are used to improve the user experience, make transportation networks work better, and control traffic flow.
Key Regions and Countries
North America
- US
- Canada
- Mexico
Western Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Portugal
- Ireland
- Austria
- Switzerland
- Benelux
- Nordic
- Rest of Western Europe
Eastern Europe
- Russia
- Poland
- The Czech Republic
- Greece
- Rest of Eastern Europe
APAC
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia & New Zealand
- Indonesia
- Malaysia
- Philippines
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
Latin America
- Brazil
- Colombia
- Chile
- Argentina
- Costa Rica
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- Algeria
- Egypt
- Israel
- Kuwait
- Nigeria
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- Turkey
- United Arab Emirates
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Uber is the world leader in ride-hailing services, and it has grown to offer other ways to get around. With the company's app, you can book rides, order food delivery, rent bikes or scooters, and in some places, you can even book tickets for public transportation. Uber is a big player in the MaaS market because it has a large number of users and a well-known name.
Lyft is another well-known ride-hailing service that has been working hard in the MaaS area. Like Uber, Lyft's app lets users choose between different ways to get around, such as standard rides, shared rides, and rentals. The company has also teamed up with public transit agencies to add their services to the Lyft app, making it easy to switch between different types of transportation.
Didi Chuxing is the most popular ride-hailing service in China, and it offers more than just rides. The company has bike-sharing, car-sharing, and shuttle services, so people can choose how they want to get around. Didi Chuxing is a big player in the global MaaS market because it has a strong footprint in China.
The Finnish company MaaS Global made the MaaS platform Whim. Whim is an app that lets people plan, book, and pay for different kinds of transportation, like cabs, rental cars, and bikes, all in one place. Whim works in a number of places around the world, and its comprehensive approach to MaaS has earned it a lot of praise.
Top Key Players in Mobility as a Service Market
- Uber Technologies Inc.
- Didi Chuxing Technology Co., Ltd.
- Lyft Inc.
- Gett, Inc.
- Mytaxi
- Ola Cabs
- BlaBlaCar
- Careem
- Kakao Corp.
- Addison Lee Limited
- MERU Cabs
- Via Transportation Inc.
- Yandex N.V. (Yandex.Taxi)
- LeCab SAS
- Ingogo PTY LTD
- Flywheel Software, Inc.
- Easy Taxi Serviços Ltd.
- Gocatch
Recent Development
- In 2022, Ford and Lyft started a test project for MaaS in Miami. Through the FordPass app, Ford customers can book Lyft rides as part of the scheme.
- In 2022, Together with Moovit, Volvo Cars is putting out a MaaS app in Europe. With the app, Volvo users will be able to book rides from a wide range of services, such as public transit, taxis, and car-sharing services.
- In 2023, Waymo started a test program for MaaS in Phoenix. Waymo customers can use the program to book rides from a range of services, such as public transportation, taxis, and car-sharing services.
- In 2023, Together with Uber, Apple is adding ride-hailing to its Maps app. With this connection, Apple Maps users will find it easier to book Uber rides.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2022) USD 230 Bn Forecast Revenue (2032) USD 1,062.9 Bn CAGR (2023-2032) 17% Base Year for Estimation 2022 Historic Period 2016-2022 Forecast Period 2023-2032 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Service Type(Ride Hailing, Car Sharing, Others), By Operating System(Android, iOS, Others), By Transportation Type(Private, PublicBy Solution Type, Technology Platforms, Payment Engines, Others) Regional Analysis North America – The US, Canada, & Mexico; Western Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Ireland, Austria, Switzerland, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Western Europe; Eastern Europe – Russia, Poland, The Czech Republic, Greece, & Rest of Eastern Europe; APAC – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia & New Zealand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, & Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Argentina, Costa Rica, & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Kuwait, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Uber Technologies Inc., Didi Chuxing Technology Co., Ltd., Lyft Inc., Gett, Inc., Mytaxi, Ola Cabs, BlaBlaCar, Careem, Kakao Corp., Addison Lee Limited, MERU Cabs, Via Transportation Inc., Yandex N.V. (Yandex.Taxi), LeCab SAS, Ingogo PTY LTD, Flywheel Software, Inc., Easy Taxi Serviços Ltd., Gocatch Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) -
-
- Uber Technologies Inc.
- Didi Chuxing Technology Co., Ltd.
- Lyft Inc.
- Gett, Inc.
- Mytaxi
- Ola Cabs
- BlaBlaCar
- Careem
- Kakao Corp.
- Addison Lee Limited
- MERU Cabs
- Via Transportation Inc.
- Yandex N.V. (Yandex.Taxi)
- LeCab SAS
- Ingogo PTY LTD
- Flywheel Software, Inc.
- Easy Taxi Serviços Ltd.
- Gocatch




